The right amount of sugar or glucose in our blood generates energy, allowing the organs and cells to function. Any fluctuation in the blood sugar level can be harmful to the body. Serious complications such as diabetes and heart failure or stroke arise from high blood sugar levels. However, to lead a healthy lifestyle and manage diabetes, prescription-based medication, diet and regular exercise play a significant role.
What you should know:
What is diabetes?

Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the blood sugar level is too high owing to insulin resistance. The existence of high blood sugar is known as hyperglycaemia, whereas low blood sugar level is termed hypoglycaemia.
Diabetes is of three types: Type 1 diabetes, which is primarily diagnosed during childhood, is when the body is incapable of creating insulin; type 2 diabetes or diabetes mellitus wherein the body resists insulin, and gestational diabetes which occurs in pregnant women.
The targeted blood sugar level for individuals without diabetes before a meal is 72-99 mg/dl and 2 hours after a meal is less than 140 mg/dl, whereas that for people with diabetes is 80-130 mg/dl and less than 180 mg/dl, respectively.
It is important to take into consideration the cohort that is at a higher risk of developing diabetes. They include people in the age bracket of 45 years or older, overweight or obese, as a result of a sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart diseases. Your blood sugar level may rise if you become inactive, miss a dose of insulin or oral glucose-lowering medicine.
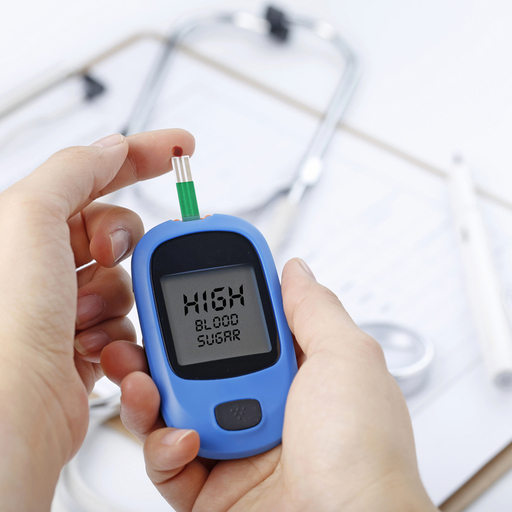
Symptoms of high blood sugar level

Here are the early symptoms of high blood sugar levels:
- Frequent Urination – In case of high blood sugar levels, the kidneys expel the excess blood sugar, causing you to urinate frequently.
- Increased Thirst – Since your kidneys are getting rid of the excess sugar, valuable fluids are pulled from your tissues, resulting in dehydration and increased thirst.
- Fatigue – Excess of blood sugar also affects the way your body uses glucose, leading to exhaustion and fatigue.
- Affects Vision – High blood sugar can damage the blood vessels of the eye, resulting in a swollen lens, causing a blurry vision or even blindness if not cured timely.
- Weight Loss – Glucose is a source of energy for our body. Due to glucose discharge, the body is unable to gain energy, which leads to burning fat and muscle and unexplained weight loss.
- Hyperglycaemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS) – High blood sugar can also lead to this deadly condition wherein the body cannot process sugar.
- Nerve damage – Hyperglycaemia can impact your nerves, causing a tingling sensation or numbness in the hands and feet and can escalate to neuropathy over time.
- Yeast infection, skin discolouration, kidney failure and a weakened blood circulation system, lead to the slow healing of cuts and wounds.
Take charge of your blood sugar level

Learn how to keep your blood sugar level under control:
- Consume a balanced diet and follow your meal plan. Keep a count of your carbs intake for every meal.
- Regularly exercise for at least 30 minutes or practice yoga and meditation.
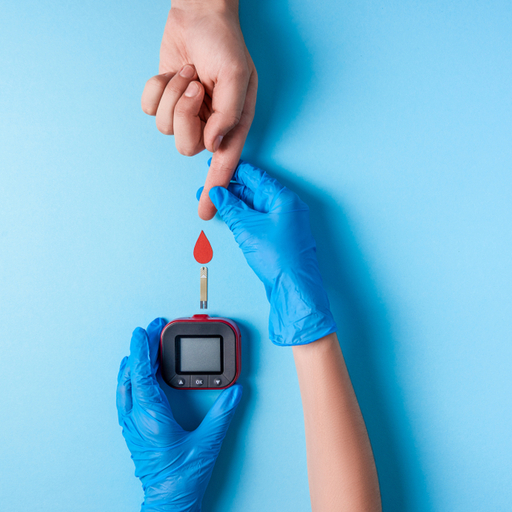
- Test your blood sugar regularly.
- Stay hydrated.
- Consult your doctor in case the blood sugar level is not controlled.
You can also measure your blood sugar level on our Blood Sugar Level Calculator. Get more nutrition and lifestyle-related information for your physical and mental well-being on our Activ Living Page.





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000









Thank you for sharing your expertise. I found your post very enlightening.