It is widely known that cholesterol plays a significant role in maintaining your heart health, making it one of the most pressing health concerns of today.
What you need to know:
- What is cholesterol?
- What is LDL cholesterol?
- What causes high LDL cholesterol?
- Foods to avoid to reduce LDL cholesterol
- Tips to cut your cholesterol levels
What is cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the cells of the body. It is a type of lipid (fat) essential for the proper functioning of the body. Your body uses cholesterol to create cell membranes, hormones, and vitamin D. Cholesterol is derived from two sources: it is produced by the liver and can be obtained from various animal-based foods, such as meat, poultry, and dairy products. Some of these foods contain high levels of saturated and trans fats, which cause your liver to make more cholesterol than it otherwise would. This added production increases normal cholesterol levels to one that is unhealthy.
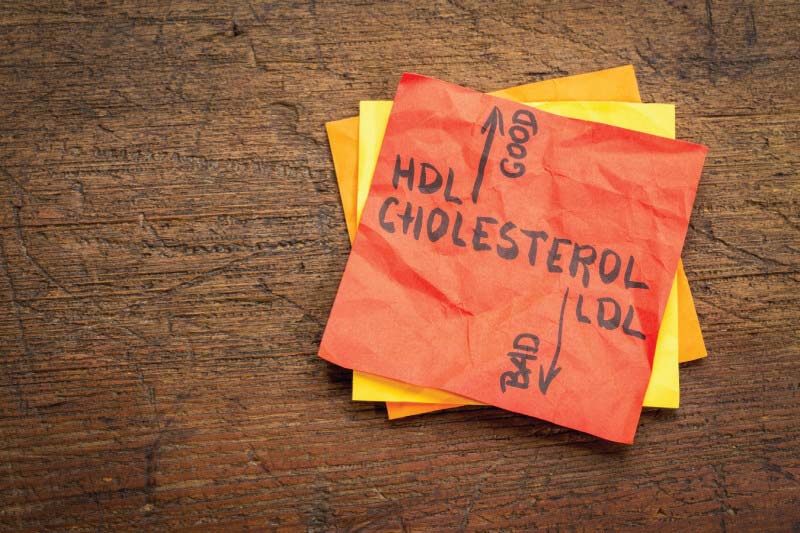
Types of cholesterol
Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream on proteins called lipoproteins (particles in the blood made up of lipids and proteins). There are two main types of lipoproteins: High-density lipoprotein (HDL) and Low-density lipoprotein (LDL).
HDL is known as ‘good’ cholesterol because it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and carries it back to the liver, where it is either broken down or passed out of the body as a waste product.
What is LDL cholesterol?
LDL, also referred to as ‘bad’ cholesterol, as the name suggests is bad for the body. It is a combination of fat and protein that transports cholesterol from the liver to other body parts, including the arteries. High cholesterol has no symptoms. The only way to detect it is through a blood test called a ‘lipid profile’. To determine your total cholesterol and for accurate results, ensure you follow the given pointers before the test,
- Avoid any strenuous activity
- Fast for at least 9-12 hours
- Inform the doctor about any medical conditions or medications
Healthcare providers use the following categories to describe your LDL cholesterol level:
- Normal: Below 100 mg/dL
- Near-optimal: 100 – 129 mg/dL
- Borderline high: 130 – 159 mg/dL
- High: 160 – 189 mg/dL
- Very high: 190 mg/dL or higher
Men are at a higher risk of high cholesterol than women. However, the menopause phase can increase the risk of high cholesterol in women. The risk of high cholesterol increases for men between the ages of 45-65 and women between 55-65.
Effects of high LDL cholesterol
The consequences of high LDL cholesterol levels cannot be downplayed. It can lead to a number of negative consequences, including:
- Cardiovascular disease: When LDL cholesterol is deposited in the walls of the arteries, the plaque build-up in them causes the arteries to narrow and become less flexible, resulting in a condition known as atherosclerosis. High amounts of bad cholesterol can clog up a critical path, restricting the blood flow to the heart, brain, and the rest of the body, which can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications;
- Peripheral Artery Damage (PAD) is a condition in which the arteries in the legs become narrow or blocked, causing leg pain, cramping, and difficulty walking;
- In addition, coronary heart disease, accompanied by other issues like smoking, high blood pressure (hypertension), or diabetes, puts you at a higher risk of severe health problems.
What causes high LDL cholesterol?
Many factors can be linked to heart problems or strokes. These include:
Poor diet
An unhealthy diet high in saturated and trans fats can increase cholesterol levels in the body.
Lack of physical activity
A sedentary and inactive lifestyle can contribute to high cholesterol levels.
Obesity
People who are obese or overweight tend to have high LDL cholesterol levels. Obesity can cause insulin resistance, making the body less sensitive to insulin. Thus, it can lead to higher levels of triglycerides and LDL cholesterol in the body.
Smoking
A toxic chemical called acrolein, found in cigarettes, damages the blood vessel lining and increases the level of oxidative stress in the body, leading to the formation of oxidized LDL cholesterol. Oxidized LDL is more prone to stick to the artery walls, forming fatty deposits and plaques. Additionally, acrolein can stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and other pro-inflammatory molecules, which promotes the oxidation of LDL cholesterol.
Genetics
High cholesterol levels can run in families. Individuals may inherit the genes that cause their bodies to produce more cholesterol. Hypercholesterolemia is an inherited condition that may occur in some individuals despite consuming healthy food daily.
Medical conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hyperthyroidism, and liver or kidney disease, can increase cholesterol levels.
Medications
Certain diuretics or beta-blocker medications can also increase cholesterol levels in the body.
Types of foods to avoid to reduce LDL cholesterol
Lowering LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is crucial for maintaining heart health. Here are key foods to limit:
Saturated Fats
These fats come primarily from animal sources such as red meat, pork, and full-fat dairy products, including butter, cheese, and milk. Limiting consumption can help reduce LDL levels.
Processed Meats
Items like sausages, hot dogs, and bacon are high in saturated fats and sodium, which can exacerbate cholesterol levels. Opt for leaner cuts or plant-based alternatives.
Desserts and Sweets
Cookies, cakes, ice cream, and candies are not only rich in unhealthy fats but also sugars, contributing to weight gain and higher LDL cholesterol. Enjoy these treats sparingly.
Fast Food
Typically high in calories, saturated fats, and trans fats, regular fast food consumption can lead to increased LDL cholesterol. Choose healthier, lower-cholesterol options when eating out.
Avoiding these foods and choosing healthier alternatives can help manage your bad cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart disease.
Tips to cut your cholesterol levels

Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet is the first step to reducing cholesterol. Follow the given tips to lower your cholesterol levels –
Ban trans fats
Trans fats are a type of unsaturated fat that can increase LDL cholesterol levels in the body. Cut down on foods that include trans or saturated fats. Some of them are listed as follows:
- Fried foods, such as french fries, doughnuts, fried chicken, or foods cooked in hydrogenated oils
- Margarine, especially those that are solid at room temperature
- Baked goods, like cakes, pastries, and muffins
- Packaged snacks, like crackers, chips, and cookies, which often contain partially hydrogenated oils
- Fast foods, including burgers and tacos
- Butter, ghee, lard
Scale back
Inactive individuals are more likely to develop LDL cholesterol. Eat a balanced diet replete with whole grains, lean protein, fruits and vegetables. Be mindful of your portion sizes. Use small plates and avoid going back for second helpings.
Get moving
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Regular physical activity can help improve cholesterol levels by increasing the production of enzymes that help break down triglycerides and LDL cholesterol in the blood.
Consume fishes
Fatty fish are a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fat that can lower LDL cholesterol. Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and lower triglycerides, which can help reduce LDL cholesterol levels. Some examples of fatty fish include tuna, salmon, sardines, and mackerel.
Go nuts
Consuming almonds, walnuts, peanuts, and other types of nuts can benefit your heart health. Nuts are a rich source of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help lower harmful cholesterol levels in the blood. They are also a good source of fiber and a powerhouse of antioxidants, which can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are linked to heart health.
Incorporate mindfulness practises
Following a healthy diet does not suffice. Incorporate specific lifestyle changes to lower your cholesterol level. Get adequate sleep of at least 7-8 hours to avoid weight gain. Practise yoga and mindfulness meditation to reduce stress.
It is essential to check your cholesterol regularly to ensure it is at a healthy level. You can determine your total cholesterol through our online Total Cholesterol Calculator.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Stay updated with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, high Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruaat ABHIkaro.
You may also like to read blogs on:
- How Can You Lower The Level Of Bad Cholesterol This Summer Season?
- What are the 4 lifestyle changes you can make to lower your cholesterol levels?
Popular Searches
Natural Beta blockers | How to cure depression | Summer activities for kids | High bp symptoms | HIIT workout | How to increase platelet count | Dash diet | Systolic and diastolic blood pressure | High blood sugar symptoms | Tabata workout | Push ups for beginners | Benefits of zumba | How to prevent breast cancer | Homeopathic medicine for asthma | Fruits to avoid in pcos | Neck pain relief exercises |Yoga for heart | Healthy soup recipes | Anti aging foods | Vitamin rich foods





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000









