What is insulin resistance? It is a health condition where the body starts to turn a blind eye to insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. This condition can happen because of genetic predispositions and lifestyle choices.
What you need to know:
- What is insulin resistance?
- The importance of insulin and its role in blood sugar control
- Insulin resistance symptoms
- Insulin resistance diet: what to eat and avoid
- Preventing insulin resistance
- Understanding the risks of untreated insulin resistance
What is insulin resistance?

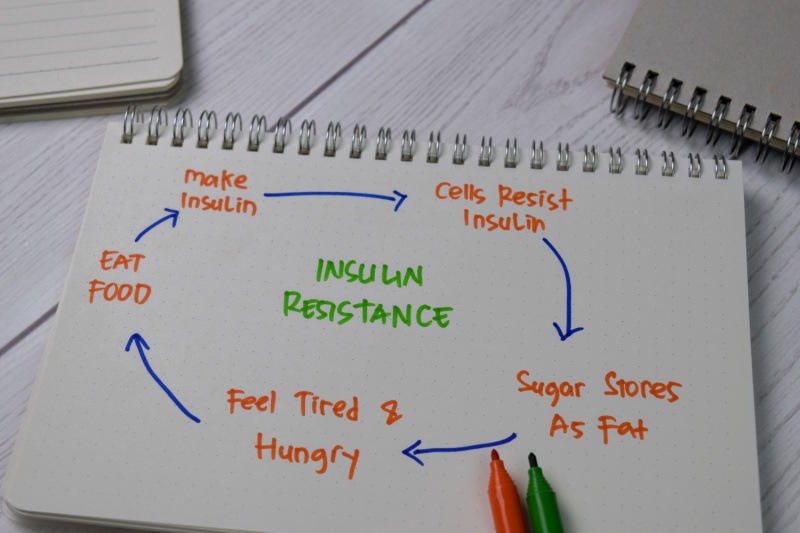
Insulin resistance occurs when your body, muscle, and liver cells have reduced insulin response, a vital hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in life-sustaining functions and blood glucose (sugar) level regulation. This condition can be temporary or a chronic issue. In most instances, it is manageable and treatable.
Under normal conditions, insulin operates in a sequential manner:
- The body converts consumed food into glucose (sugar), serving as the primary energy source.
- The presence of glucose in the bloodstream enables the pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin assists in the transportation of glucose into the cells of muscles, fat, and the liver for energy utilization.
- As glucose enters the cells, reducing your blood glucose levels, a signal is sent to the pancreas to halt insulin production.
Key factors contributing to insulin resistance
Here are some of the key factors that can cause insulin resistance:
- Obesity
- A family history of diabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
- A history of gestation diabetes
The importance of insulin and its role in blood sugar control
Insulin plays a vital role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels in your body –
How insulin works in the body
- Your body breaks down the food you eat into glucose, your body’s main source of energy.
- Glucose enters your bloodstream, signaling your pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin helps glucose in your blood enter your cells so they can use it for energy or store it for later use.
- The levels in your bloodstream decrease, signaling your pancreas to stop producing insulin.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels
Your blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, but insulin keeps them within a healthy range. When your body does not absorb or convert enough glucose, blood sugar levels remain high. Insulin reduces your body’s blood sugar levels and provides cells with energy by helping cells absorb glucose.
Insulin resistance symptoms
Here are some of the insulin resistance symptoms that you can experience when you have hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), including:
- Increased water intake
- Frequent peeing
- Increased hunger levels
- Slow-healing cuts and sores
- Blurry vision
- Headaches
- Skin infections
Insulin resistance diet: What to eat and avoid
Here are the types of food that you can consume when you have insulin resistance:
- Vegetables: Consume dark, leafy greens such as spinach as they are low in both carbs and calories but rich in nutrients, allowing you to eat substantial amounts.
- Fruits: Fruits are an excellent option for people with insulin resistance as they are filled with essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. For a dessert, try adding berries to plain, non-fat yogurt.
- High fiber intake: Aim to consume 21 to 25 grams of fiber daily for women and 30-38 grams for men, as it can assist in maintaining balanced blood sugar levels. Almonds, black beans, broccoli, lentils, and oatmeal are excellent high-fiber choices.
- Moderation in carbs: Carbohydrates are still on the menu, but it’s important to choose wisely and consume them in moderation. Prioritize carbs from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and low-fat dairy over processed foods like white bread and pasta.
Here are some of the foods to avoid:
- Processed food
- Refined sugar
- Saturated fats and trans fats
- Sweetened fizzy drinks
Preventing insulin resistance
Here are some of the ways to prevent insulin resistance:
Effective lifestyle changes for controlling insulin resistance
These lifestyle changes can help you manage insulin resistance in a much better way:
- Staying active: Regularly engage in moderate-intensity physical activities to use glucose more efficiently and improve how your muscles respond to insulin.
- Manage your weight: Your healthcare provider might recommend shedding some weight to deal with insulin resistance. Managing excess weight can slash your risk of developing type-2 diabetes by a whopping 58%
- Adopt a nutritious diet: Consult a nutritionist, who may suggest you reduce carbs intake, as they can cause your body to produce more insulin than needed. Instead, focus on a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fish, and lean proteins.
Understanding the risks of untreated insulin resistance
When your body does not respond to insulin as it should, it creates an imbalance in your blood sugar levels. Let us now understand the potential risks that can develop if it is left untreated –
Development of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes
Prediabetes is a condition in which your blood sugar is high, but not high enough to be type 2 diabetes. In a person with prediabetes, the pancreas works increasingly hard to release enough insulin to overcome the body’s resistance and keep blood sugar levels down. Over time, the pancreas loses its ability to release insulin, and this can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Increased risk of heart disease
Insulin resistance raises blood sugar levels, and high blood sugar leads to inflammation, which damages the lining inside arteries. That damage could make it easier for plaque to build up in arteries. High blood sugar and inflammation also damage the nerves that control your heart. All of these changes can lead to diseases in your heart and blood vessels.
Other potential health complications
There are also links between insulin resistance and the following health issues –
- Acanthosis nigricans – In this disorder, thick, velvety patches form on your groin, armpits, and back of your neck.
- PCOS (Polycystic ovary syndrome) – The symptoms of PCOS can include irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and periods that cause pain.
- Major depressive disorder (MDD) – High levels of insulin in your blood increase your risk for developing a major depressive disorder.
Lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management, are crucial in managing insulin resistance.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Keep up to date with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruat ABHI karo.
You may also be interested in the following blogs:
- Is Papaya Good For Diabetes? Discover 3 Surprising Benefits For Blood Sugar Management
- Do Bananas Affect The Blood Sugar Levels Of People With Diabetes?
Popular Searches
How to lower blood pressure | Fruits good for liver | Unhealthy foods | Ragi Benefits | Basal Metabolic Rate | Acupressure points for High Blood Pressure | Ayurvedic medicine for blood pressure | How to control cholesterol at home | Homeopathy for Asthma | Biological Age | Home remedies for TB | Natural beta blockers | Negative effects of internet | Types of walking | Blood pressure calculator | Blood sugar calculator | BMI Calculator





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000






