You must have noticed a swelling or redness in your skin after an injury. It might be due to inflammation.
What you need to know:
- What is inflammation?
- Types of inflammation
- Common causes of inflammation
- Inflammation symptoms
- Inflammation treatment and prevention
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is a process by which your body’s white blood cells and their production protect you from injury or infection from outside invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. It promotes healing and helps you feel better. Fever, for example, is how you know your body’s inflammatory system is working correctly when you are ill. However, inflammation that happens when there’s no injury or invader can harm healthy parts of your body and cause a range of chronic diseases.
How inflammation works?
Chemicals from your body’s white blood cells enter your blood or tissues. This raises the blood flow to the area of injury or infection. It can cause redness and warmth. Some chemicals like histamine, bradykinin, and prostaglandins from white blood cells cause fluid to leak into your tissues, resulting in swelling. This protective process may trigger nerves and cause pain.
Types of inflammation
Here are some common types of inflammation explained:
Acute inflammation
This type is short-lived and goes away within hours or days. It’s a response to an illness or injury. Your body sends inflammatory cells to the site of the problem so you can start recovering. Examples of things that can trigger acute inflammation include:
- Cuts
- Viral illnesses such as the flu
- Bacterial infections such as strep throat
Chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation can last months or years, even after the thing that triggered the inflammation is gone. In certain diseases, your body’s defense system – your immune system – triggers inflammation when there are no invaders to fight off. In autoimmune diseases like arthritis, your immune system acts as if regular body tissues are infected or somehow unusual and attacks them, causing damage.
Common causes of inflammation
Let us explore some common causes of inflammation:
Lifestyle factors: Diet, exercise, and stress
Certain types of foods may lead to chronic inflammation:
- Sugar
- Refined carbohydrates
- Trans fats
- Alcohol
- An imbalance of healthy and unhealthy microbes in your gut
Low levels of physical activity and obesity can cause chronic inflammation. Chronic or long-term stress, which goes on for weeks or months, can also cause inflammation.
Infections and injuries
If you have acute inflammation, you may know exactly what caused it: an injury or a bacterial or viral infection. Some factors and infections that can lead to acute inflammation include:
- Acute bronchitis, appendicitis, and other illnesses ending in ‘-itis’
- An ingrown toenail
- A sore throat from a cold or flu
- Physical trauma or wound
Autoimmune diseases
Chronic inflammation can develop if you have autoimmune diseases. In such a disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks normal healthy tissue, as in:
- Psoriasis – a condition in which skin cells build up and form scales and itchy, dry patches.
- Rheumatoid arthritis – A long-lasting inflammatory disorder affecting many joints, including the hands and feet, or
- Lupus – An inflammatory disease caused when the immune system attacks its tissues.
Inflammation symptoms
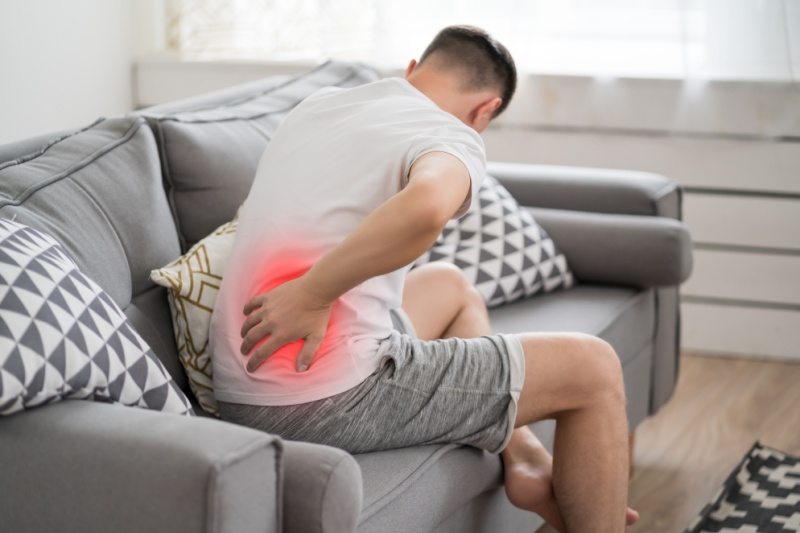

A specific part of your body might be affected, or your symptoms might be more general. When a joint is affected, the symptoms include:
- Redness
- A swollen joint that may be warm to the touch
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness
- A joint that doesn’t work as well as it should
You may develop flu-like symptoms:
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue/loss of energy
- Headaches
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle stiffness
You also might have other symptoms:
- Pain in your belly
- Rash on your skin
- Diarrhea, constipation, or acid reflux
- Sores in your mouth
- Weight gain or loss
- Depression, anxiety, or other mood disorders
Inflammation treatment and prevention
Treatment for diseases that cause inflammation may include medications, rest, exercise, and surgery to correct joint damage. Your treatment plan will depend on several things, including your type of disease, age, medications you take, overall health, and how severe the symptoms are.
Lifestyle changes for reducing inflammation
Consider the following lifestyle modifications:
- Watch your weight and stay active – Consuming too many calories and being overweight, especially around your belly, leads to greater levels of inflammatory compounds.
- Focus on fat type – Trans fats in fried foods, and saturated fats in full-fat dairy foods contribute to chronic inflammation. Omega-3 fats exert anti-inflammatory effects.
- Eat more unrefined carbohydrates – like colorful fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid alcohol – It may exert an inflammatory effect.
Medical interventions for chronic inflammation
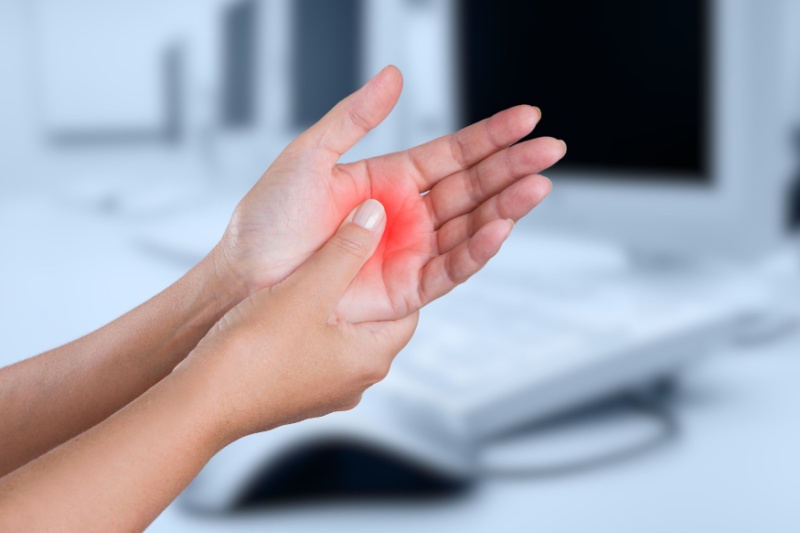

Many drugs can ease pain and swelling. They also may prevent or slow inflammatory disease. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve pain, swelling, fever, and other symptoms. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen and aspirin. Acetaminophen, including paracetamol or Tylenol, can relieve pain but not reduce inflammation. These drugs allow the inflammation to continue its role in healing. Corticosteroids, such as cortisol, are a type of steroid hormone. They affect various mechanisms involved in inflammation.
Natural remedies and supplements
Some remedies to ease long-term inflammation include the following:
- Quit smoking.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Manage stress.
- Get regular physical activity.
- Try supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, green tea, or capsaicin. Magnesium and vitamins B6, C, D, and E also have some anti-inflammatory effects. Talk to your doctor before starting any supplement.
Eat foods that reduce inflammation, such as:
- Tomatoes
- Olive oil
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach)
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts)
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, sardines)
- Fruits (berries, oranges)
Inflammation is your body’s response to an injury or illness, or the perception of one. Keeping the aforementioned in mind, you can deal with it better.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Keep up to date with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruat ABHI karo.
You may also be interested in the following blogs:
Popular Searches
How to lower blood pressure | Fruits good for liver | Unhealthy foods | Ragi Benefits | Basal Metabolic Rate | Acupressure points for High Blood Pressure | Ayurvedic medicine for blood pressure | How to control cholesterol at home | Homeopathy for Asthma | Biological Age | Home remedies for TB | Natural beta blockers | Negative effects of internet | Types of walking | Blood pressure calculator | Blood sugar calculator | BMI Calculator





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000