When you feel like you are pushing during a tough workout, give yourself an extra pat on the back. Why? Because your hard work doesn’t stop when you do.
What you need to know:
- What is the afterburn effect?
- Factors affecting the afterburn effect
- Possible treatment and recovery options
- Common misconceptions about afterburn
What is the afterburn effect?
During intense exercise, your metabolic rate increases. When you stop, it doesn’t return to a resting state immediately but remains elevated shortly. This causes an increase in calorie burn, even after you have stretched, showered, and eaten your post-workout snack. The additional energy expenditure after your workout is known as the afterburn effect. Afterburn or excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), also known as oxygen debt, is the oxygen required to return the body to its resting state. This resting state includes:
- restoring oxygen levels
- removing lactic acid
- repairing muscle and restoring levels of adenosine triphosphate (ATP – a molecule that provides the body with energy for processes like exercise)
The afterburn effect is a beneficial phenomenon that aids in weight loss and helps build muscles. One study demonstrated that it could persist for up to 38 hours.
Factors affecting the afterburn effect
How many calories you burn during the afterburn depends on the following factors:
Intensity and duration of exercise

The more intense your workout, the more expenditure it will take to return your body to rest. This means greater EPOC. Also, performing more exercises in less time tends to have a greater afterburn effect than a steady-state workout. The key to inducing significant EPOC is high-intensity interval training or HIIT. These include short rounds of intense work with equally short recovery periods.
Fitness level and body composition
Other factors that alter your afterburn rewards include weight, fitness level, and muscle mass. If you are aerobically fit, your body will be a better fat burner. You will have a more sustained afterburn effect. Obesity is a long-term condition defined by an excess amount of body fat. If you are overweight or obese, you tend to have a lower afterburn effect. If you have more muscle mass, you will have a greater afterburn effect than those with lower muscle mass.
Recovery and nutrition
During the recovery phase after exercise, your body uses oxygen and calories to repair muscles and replenish stores of oxygen and ATP. This is what causes the afterburn effect. Adequate nutrition can help you recover. Have a drink or snack like smoothies, protein shakes, yogurt, or bananas with a carbohydrate and protein ratio of 3:1 or 4:1 within 30-45 minutes of your workout. This boosts your energy and prepares you for the next day’s workout.
Possible treatment and recovery options
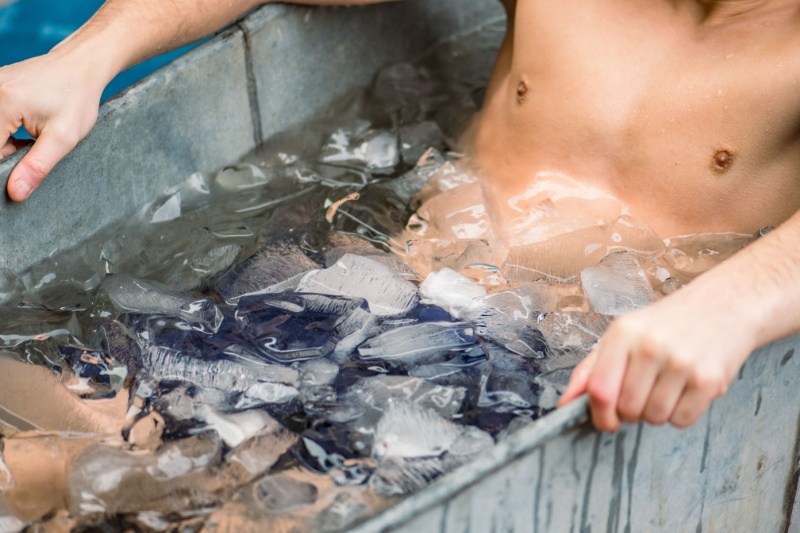

Significant afterburn can make you feel tired, which can make you feel less motivated to work out again. Here’s how to ensure a speedy recovery from a highly intense workout:
- Hot and cold treatments: Getting heat treatments through sauna baths or hot tubs helps improve blood circulation and repair muscles. Another alternative is to use cold treatment using ice packs or ice baths. Post-workout cold treatment can help soothe inflamed muscles.
- Massage: Use foam rolls, a massage stick, or even a tennis ball to apply appropriate pressure to the muscle tissue and improve circulation. Even getting a massage from a massage therapist can help.
- Sleep: During deep sleep, your body produces substances needed for tissue repair. Getting a good night’s sleep after a high-intensity workout ensures a speedy post-workout recovery.
- Alternating your workouts: You can alternate high-intensity workouts with moderate or low-intensity exercises every few days. You can also gradually build up the intensity of your exercises until you reach your goal. For example, if you want to run 5 miles a day, you can start with running one mile, then slowly add half a mile each day until you reach 5 miles.
- Compression clothing: Wearing tightly fitted clothing (compression clothing) during workouts can improve blood circulation to your muscles and help rebuild muscles faster afterward.
Common misconceptions about afterburn
Afterburn is often misunderstood. Here are some common myths and facts:
- Myth: Carbohydrates prevent the afterburn effect.
Fact: Whether or not you eat carbohydrates, the fat burns after an intense training session.
- Myth: Afterburn equals massive calorie burn.
Fact: While EPOC does increase calorie expenditure post-exercise, the effect is often overestimated.
- Myth: All workouts produce the same afterburn.
Fact: HIIT, strength training, and other intense forms of exercise produce a more significant afterburn.
- Myth: Afterburn lasts for days.
Fact: The most significant calorie burn typically occurs within the first hour after working out.
- Myth: Afterburn only occurs after HIIT.
Fact: Other forms of exercise can also result in afterburn.
- Myth: Afterburn is the key to weight loss.
Fact: It is just a part of the weight-management process.
- Myth: Afterburn is the same for everyone.
Fact: Factors like age, fitness level, metabolism, and the specific type and intensity of the workout can influence the degree of afterburn.
The afterburn effect is real. It is highest right after a workout but continues for a longer period. Steer clear of the common misconceptions about it as mentioned.
Stay tuned to the Activ Living Community. Keep up to date with the latest health tips and trends through expert videos, podcasts, articles, and much more on nutrition, fitness, mindfulness, and lifestyle conditions like Asthma, Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Diabetes. Activ Living ke saath sahi sehat ki shuruat ABHI karo.
You may also be interested in the following blogs:
Popular Searches
How to lower blood pressure | Fruits good for liver | Unhealthy foods | Ragi Benefits | Basal Metabolic Rate | Acupressure points for High Blood Pressure | Ayurvedic medicine for blood pressure | How to control cholesterol at home | Homeopathy for Asthma | Biological Age | Home remedies for TB | Natural beta blockers | Negative effects of internet | Types of walking | Blood pressure calculator | Blood sugar calculator | BMI Calculator





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000