People may flip the box and read food labels for different reasons but it’s rarely for nutritional facts. Mostly people worry about the dates of manufacture and expiry, forgetting how important it is to know what you are eating. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is responsible for setting the standards for food articles and regulating manufacture, storage, distribution and sale of food items. FSSAI also empowers the consumer with food labels to help them learn what they are eating and provides assurance that they are consuming safe and wholesome food. Food labels are pictorial or written representations of nutritional facts that are written, stenciled, printed, embossed or impressed on the food container.
Understanding Food Labels
Ensuring the safety of our food is the collective responsibility of manufacturers, producers and the government. Food labels are a way of keeping the buyer aware of the product. They lay down the nutrient content and calorific values of a product to help the buyer make healthy food choices. It is especially helpful for people with chronic illnesses who have dietary restrictions by letting them understand what they are eating. For instance, food labels are essential for diabetics since they need to avoid sugar and count carbs.
The 3 Components Of Food Labels
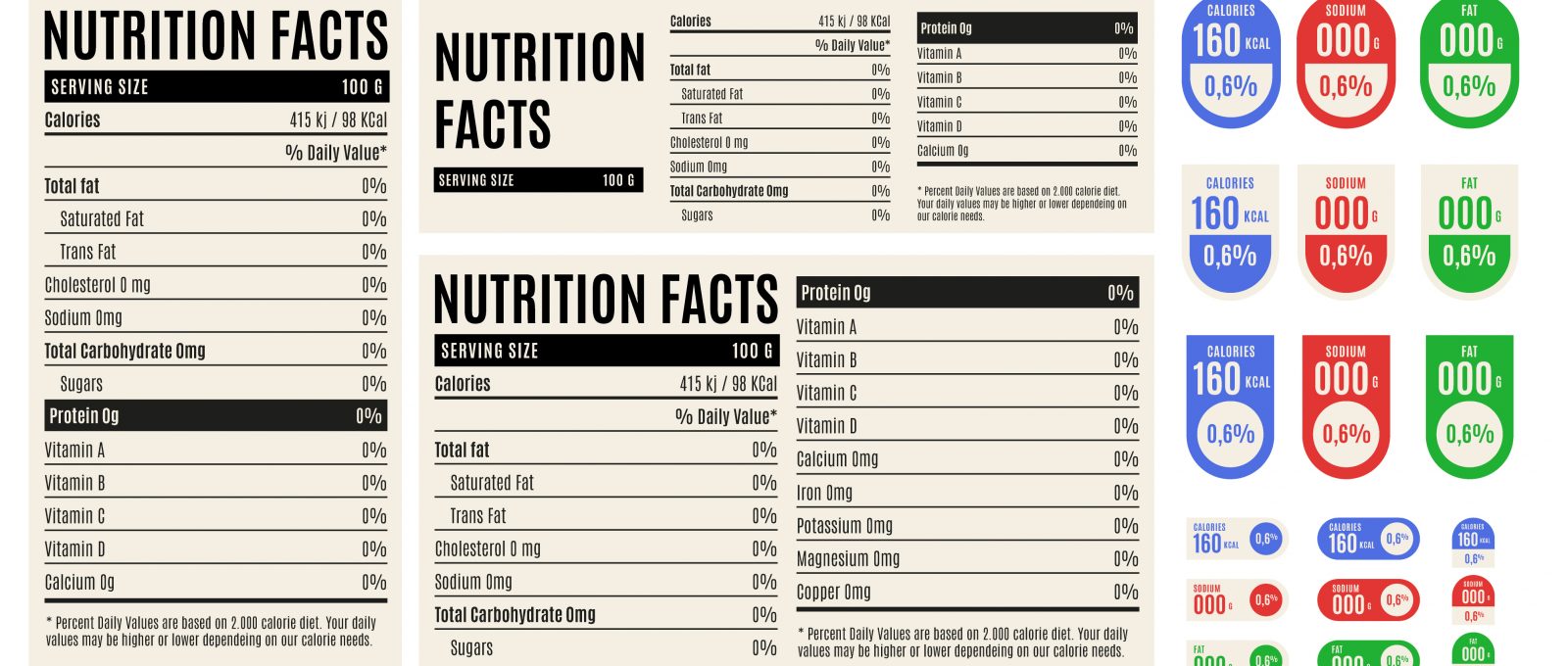
The presentation of information on the label can vary with food products or beverages. However, commonly the top section of the food label has product specific information such as calories and serving size, and there is a note at the bottom explaining % Daily Value and general advice on calories. Consumers must know how to read food labels effectively to make quick and informed decisions. The 3 components of food labels are:
- Serving Information
The first thing to look for is the serving size. Food labels mention the serving size and the total number of servings per container. Serving sizes have been standardized to easily compare similar foods. The measurements are usually mentioned in cups or spoons with a metric amount mentioned for the same. Knowing the serving size helps you understand whether you are taking more or less of that food. It does not recommend how much you should eat but certainly helps you track your servings. This is presented with the % Daily Value (%DV) to track your daily required intake. - Calories
Food calories represent the amount of energy derived from food sources. Food labels mention the amount of energy each serving provides and sometimes total energy provided by the entire food amount. The daily calorie guide is based on a 2000 calorie per day diet. The calorie information on food labels is essential for knowing how much you’re eating compared to and as a part of your daily nutrition. Calorie information on food labels is especially helpful when you’re counting calories and trying to lose weight. - Nutrients
Nutrients are listed on food labels which also represent the ingredients of the food article. This information is usually provided as per 100 grams and may have values related to lower serving sizes. Nutrients that are causes of concern are usually listed under saturated fats, added sugar and sodium. Excess consumption can lead to health complications such as diabetes, high blood pressure and cardiovascular diseases. Food labels also mention the amount of dietary fibers, vitamins, calcium, potassium and iron per serving as well as their %DV.
If you watch your added sugars then interpret the sugar labels properly. The total sugar indicates the sum of the amount of sugar naturally present in the food or beverage and the amount of sugar (such as sucrose and dextrose) added during food processing. If the amount of added sugar is zero then the total sugar represents the amount occurring naturally in the food. Reading the provided information effectively will help you support your daily personal dietary needs.





 1800-270-7000
1800-270-7000










Very usefull information